Rev0LRS
This project comprises a 433MHz (UHF) FHSS 12-Channel RC system with bi-directional link supporting a 1.6+ kbps telemetry downlink, based on the ST Microelectronics SPIRIT1 RF transceiver. The receiver features an 0.8dB NF LNA, 100 mW downlink transmitter, soft-decision Viterbi FEC (TBD), diversity switch, and RF bandpass filter with 30dB+ rejection at broadcast FM, VHF amateur, and 900-2.4GHz video.
The system aims to follow FCC rules regarding Radio Amateur (Ham) use of Spread Spectrum and RC Control, including rules governing station identification, maximum power, and telemetry. All commercial purchases of this system will be restricted to users carrying a valid amateur radio license to restrict illegal use.
System Description
The system is based around the ST Microelectronics SPIRIT1 RF transceiver. The RF PHY layer uses GMSK (Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying), with a BT (bit period) = 1, with an over-the-air data rate of 28.8/25/19.2 kbps for 12/8/4CH modes. The return (telemetry) link uses the same modulation and data rate, with a 6/5/4 byte data packet sent at 50 Hz, for an overall telemetry throughput of 2.4/2/1.6 kbps. The receiver automatically sends back the link quality and RSSI, which are both used by the receiver to determine whether a given hopping channel is clear, and is used to dynamically drop hopping channels that are noisy. If at any point the telemetry is lost, the system will function in an "open loop" frequency hopping scheme of reduced channel set (3-5 channels), such that in the event of power failure at either end, the link can be regained within ~100ms worst case. The receiver hardware features an 0.8dB NF LNA, 100 mW downlink transmitter, soft-decision Viterbi FEC (TBD), diversity switch, and RF bandpass filter with 30dB+ rejection at broadcast FM, VHF amateur, and 900-2.4GHz video.
FCC Rules
This section will provide an overview of the FCC rules governing remote control and spread spectrum transmitters[1]
§ 97.3 Definitions. (8) Bandwidth. The width of a frequency band outside of which the mean power of the transmitted signal is attenuated at least 26 dB below the mean power of the transmitted signal within the band. (46) Telemetry. A one-way transmission of measurements at a distance from the measuring instrument. § 97.217 Telemetry. Telemetry transmitted by an amateur station on or within 50 km of the Earth’s surface is not considered to be codes or ciphers intended to obscure the meaning of communications. § 97.215 Telecommand of model craft. An amateur station transmitting signals to control a model craft may be operated as follows: (a) The station identification procedure is not required for transmissions directed only to the model craft, provided that a label indicating the station call sign and the station licensee's name and address is affixed to the station transmitter. (b) The control signals are not considered codes or ciphers intended to obscure the meaning of the communication. (c) The transmitter power must not exceed 1 W. § 97.307 Emission standards. UHF: 70 cm Entire band ................. MCW, phone, image, RTTY, data, SS, test ............... (6), (8). (6) A RTTY, data or multiplexed emission using a specified digital code listed in § 97.309(a) of this part may be transmitted. The symbol rate must not exceed 56 kilobauds. A RTTY, data or multiplexed emission using an unspecified digital code under the limitations listed in § 97.309(b) of this part also may be transmitted. The authorized bandwidth is 100 kHz. (8) A RTTY or data emission having designators with A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J or R as the first symbol; 1, 2, 7 or 9 as the second symbol; and D or W as the third symbol is also authorized. § 97.311 SS emission types. (a) SS emission transmissions by an amateur station are authorized only for communications between points within areas where the amateur service is regulated by the FCC and between an area where the amateur service is regulated by the FCC and an amateur station in another country that permits such communications. SS emission transmissions must not be used for the purpose of obscuring the meaning of any communication. (b) A station transmitting SS emissions must not cause harmful interference to stations employing other authorized emissions, and must accept all interference caused by stations employing other authorized emissions. (c) When deemed necessary by a District Director to assure compliance with this part, a station licensee must: (1) Cease SS emission transmissions; (2) Restrict SS emission transmissions to the extent instructed; and (3) Maintain a record, convertible to the original information (voice, text, image, etc.) of all spread spectrum communications transmitted.
Subsection: ITU Emission Types[2]
§ 6. 1) First symbol - type of modulation of the main carrier 1.1 Emission of an unmodulated carrier N 1.2 Emission in which the main carrier is amplitude-modulated (including cases where sub-carriers are angle-modulated) 1.2.1 Double-sideband A 1.2.2 Single-sideband, full carrier H 1.2.3 Single-sideband, reduced or variable level carrier R 1.2.4 Single-sideband, suppressed carrier J 1.2.5 Independent sidebands B 1.2.6 Vestigial sideband C 1.3 Emission in which the main carrier is anglemodulated 1.3.1 Frequency modulation F 1.3.2 Phase modulation G 1.4 Emission in which the main carrier is amplitude- and angle-modulated either simultaneously or in a pre-established sequence D 1.5 Emission of pulses 1.5.1 Sequence of unmodulated pulses P 1.5.2 A sequence of pulses 1.5.2.1 modulated in amplitude K 1.5.2.2 modulated in width/duration L 1.5.2.3 modulated in position/phase M 1.5.2.4 in which the carrier is angle-modulated during the period of the pulse Q 1.5.2.5 which is a combination of the foregoing or is produced by other means V 1.6 Cases not covered above, in which an emission consists of the main carrier modulated, either simultaneously or in a pre-established sequence, in a combination of two or more of the following modes: amplitude, angle, pulse W 1.7 Cases not otherwise covered X 2) Second symbol - nature of signal(s) modulating the main carrier 2.1 No modulating signal 0 2.2 A single channel containing quantized or digital information without the use of a modulating sub-carrier 1 2.3 A single channel containing quantized or digital information with the use of a modulating sub-carrier 2 2.4 A single channel containing analogue information 3 2.5 Two or more channels containing quantized or digital information 7 2.6 Two or more channels containing analogue information 8 2.7 Composite system with one or more channels containing quantized or digital information, together with one or more channels containing analogue information 8 2.8 Cases not otherwise covered X 3) Third symbol - type of information to be transmitted 3.1 No information transmitted N 3.2 Telegraphy - for aural reception A 3.3 Telegraphy - for automatic reception B 3.4 Facsimile C 3.5 Data transmission, telemetry, telecommand D 3.6 Telephony (including sound broadcasting) E 3.7 Television (video) F 3.8 Combination of the above W 3.9 Cases not otherwise covered X
Testing
- 12.5.2013: The SPIRIT1 transceiver was assembled to the PCB and checked for shorts. The LDO, some capacitors, switches, level translators/inverters and filter were assembled and the unit was powered to check for current and functionality of the 48 MHz crystal oscillator.
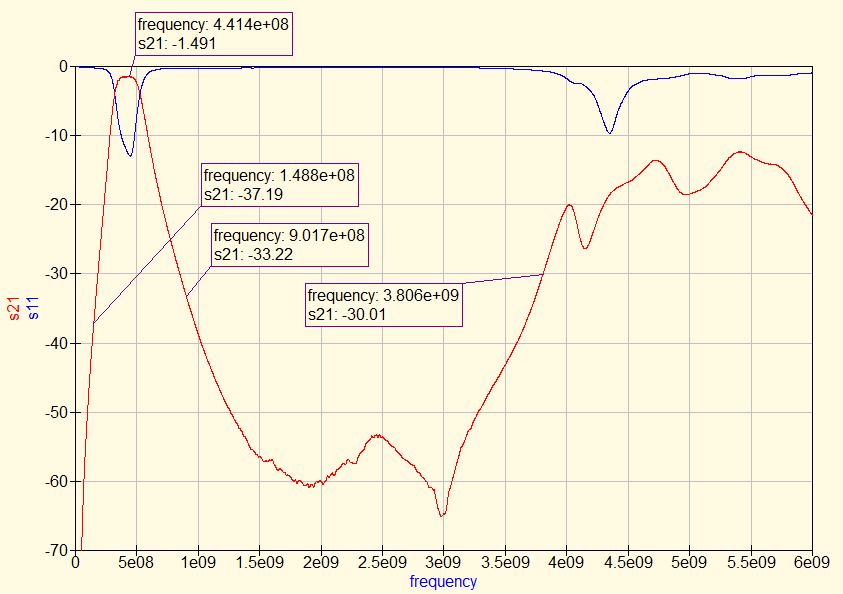
- 12.6.2013: The filter was measured for insertion/return loss, results are below. Results confirm >37 dB rejection at VHF amateur and below, and >33 dB rejection at 900 MHz ISM band and above through 3.8 GHz, with an insertion loss of <1.4 dB across the passband of 420-450 MHz.
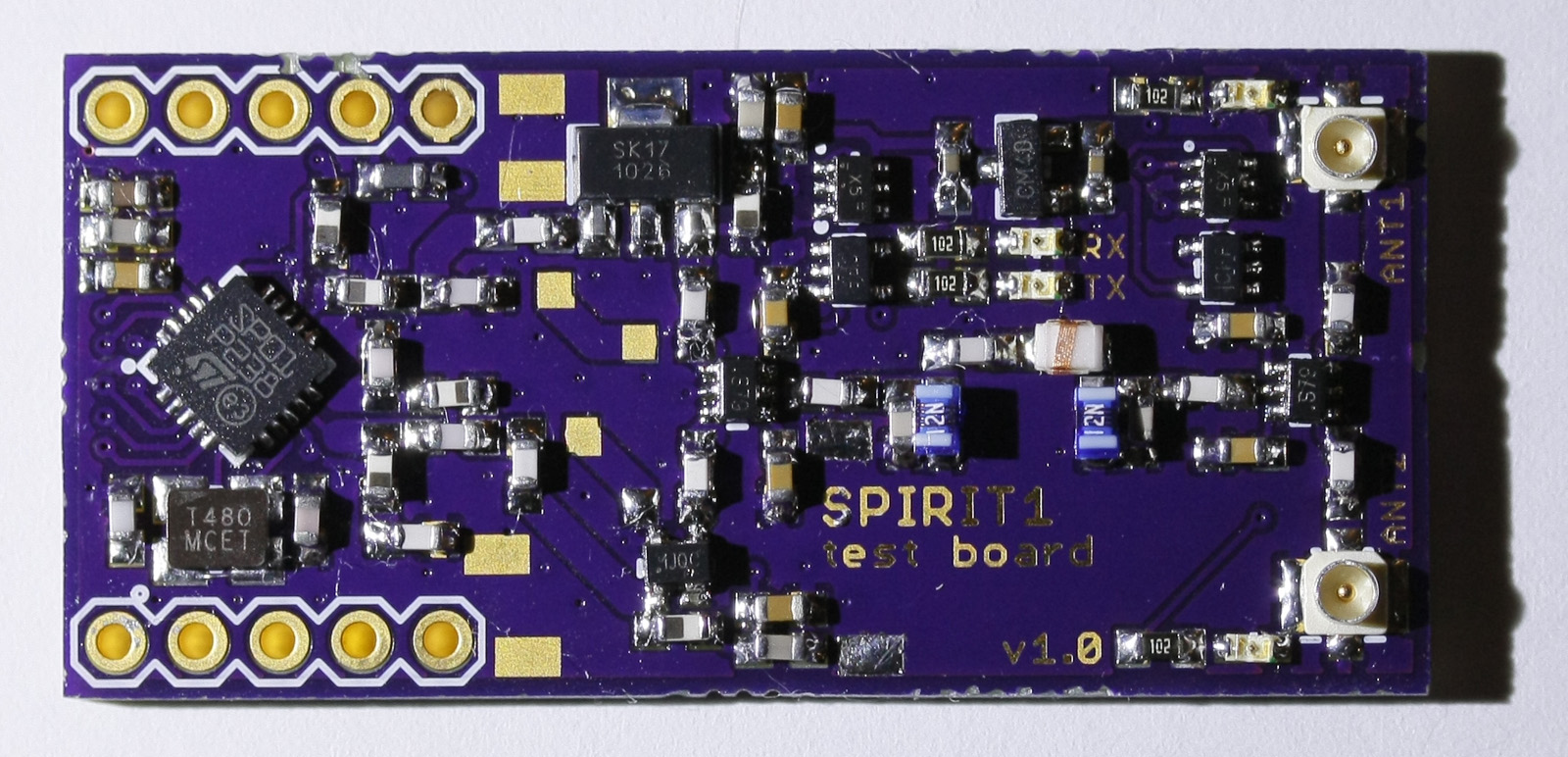
Photos
RX Bill of Materials
| IC | Quantity | Unit Cost | Total Cost | Source |
| SPIRIT1 | 1 | $4.29 | $4.29 | Digi-Key |
| MSP430F5508 | 1 | $4.54 | $4.54 | Digi-Key |
| AP1117 | 1 | $0.54 | $0.54 | Digi-Key |
| AS193-73 | 1 | $0.86 | $0.86 | Digi-Key |
| SPF5043Z | 2 | $3.22 | $6.44 | Digi-Key |
| Passive | Quantity | Unit Cost | Total Cost | Source |
| 0805 12nH Inductor | 4 | $0.22 | $0.88 | Digi-Key |
| 0603 16nH Inductor | 2 | $0.40 | $0.80 | Digi-Key |
| 0805 27nH Inductor | 2 | $0.228 | $0.46 | Digi-Key |
| 0805 56nH Inductor | 2 | $0.228 | $0.46 | Digi-Key |
| 0603 100nH Inductor | 2 | $0.082 | $0.16 | Digi-Key |
| 0603 2pF Capacitor | 2 | $0.20 | $0.40 | Digi-Key |
| 0603 2.7pF Capacitor | 1 | $0.256 | $0.26 | Digi-Key |
| 0603 3.9pF Capacitor | 2 | $0.20 | $0.40 | Digi-Key |
| 0603 10uF Capacitor | 4 | $0.264 | $1.06 | Digi-Key |
| 0603 Capacitor | 29 | $0.0096 | $0.28 | eBay - mib_instruments |
| 0603 Resistor | 19 | $0.00294 | $0.06 | eBay - mib_instruments |
| Component | Quantity | Unit Cost | Total Cost | Source |
| SMD 26MHz Crystal | 1 | $0.94 | $0.94 | Digi-Key |
| 0603 Green LED | 2 | $0.11 | $0.22 | Digi-Key |
| 0603 Red LED | 1 | $0.13 | $0.13 | Digi-Key |
| Male Header | 37 | $0.01 | $0.37 | eBay |
| SMA Male Connector | 2/5 | $2.51 | $1.00 | Dealextreme |
| PCB | 1.225"x2.275"/3 | $5.00 | $4.65 | OSH Park |
| Total Unit Cost | $29.20 |
References
- ↑ Federal Communications Commission, "Title 47— Telecommunication" Oct. 1, 2012. Available: http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/CFR-2012-title47-vol5/pdf/CFR-2012-title47-vol5-chapI.pdf
- ↑ International Telecommunication Union, "APPENDIX 1 Classification of emissions and necessary bandwidths" 2005. Available: http://life.itu.int/radioclub/rr/ap01.htm