Ryobi40V: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "This is a basic analysis of how a Ryobi 40V smart charger (model number OP403) communicates with the battery's BMS to enable the charging FET. ==Electronics== Pictures of the...") |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
[[File:Ryobi_40VChg_PCB_Bot.jpg|thumb|center|400px|PCB bottom side.]] | [[File:Ryobi_40VChg_PCB_Bot.jpg|thumb|center|400px|PCB bottom side.]] | ||
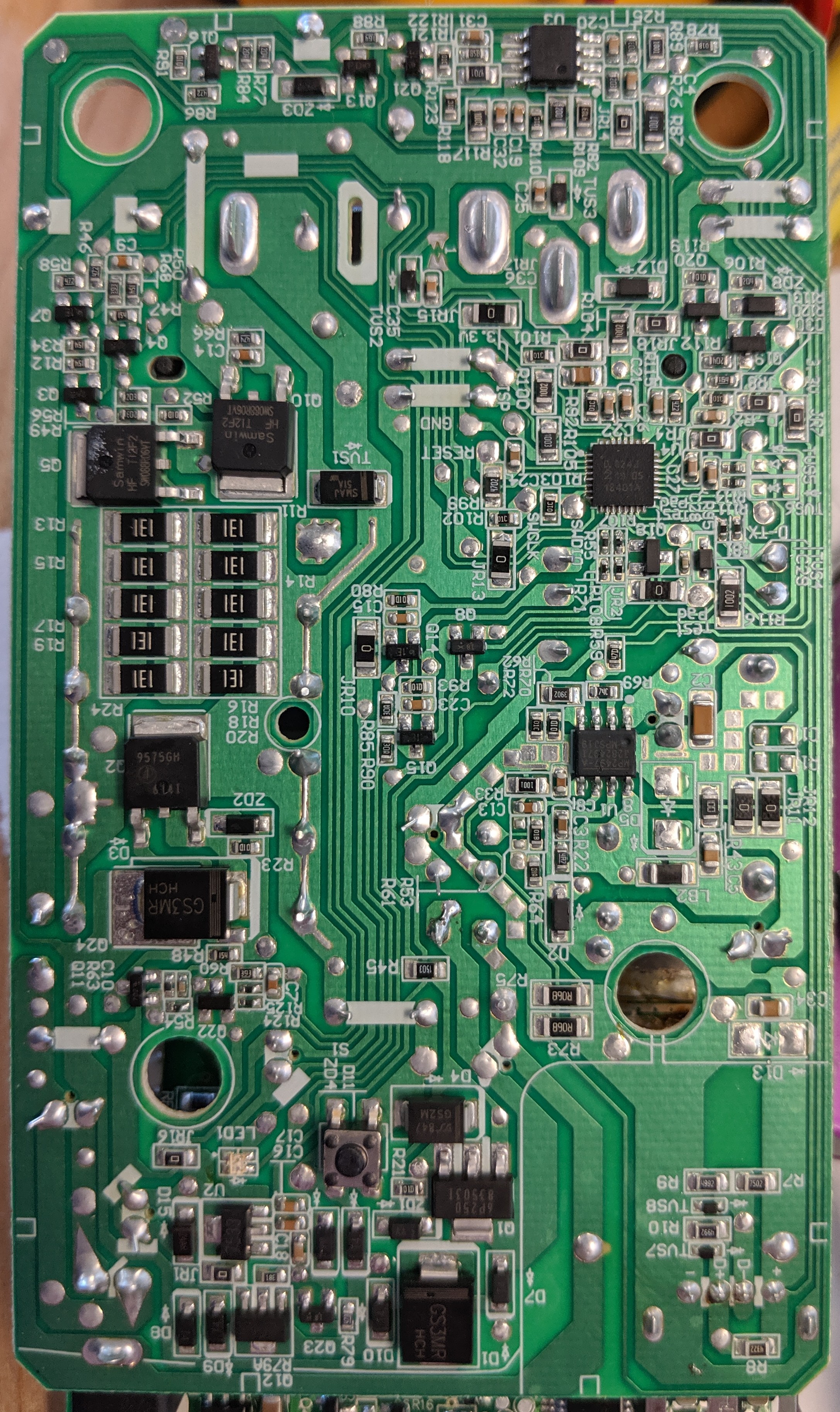
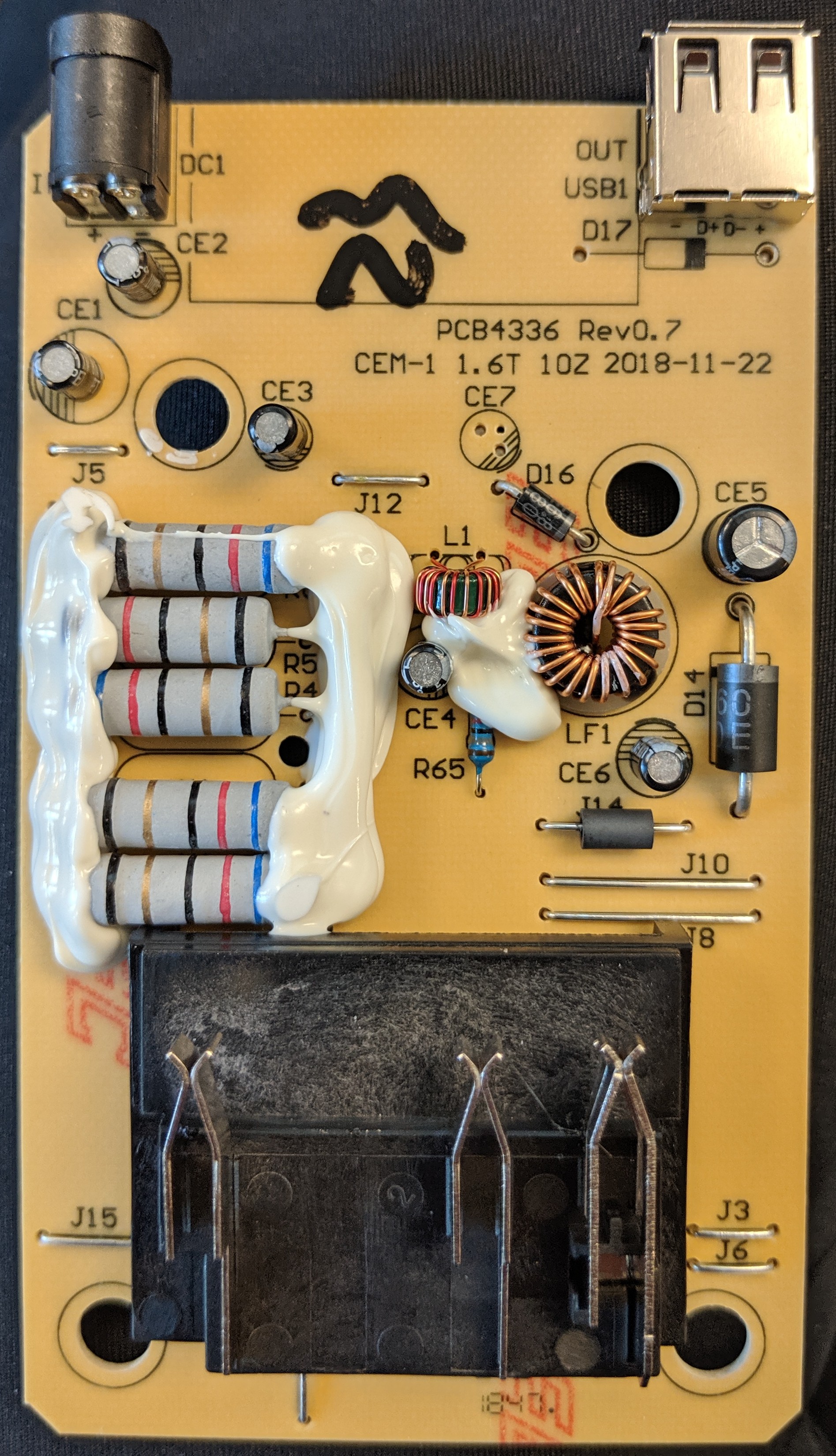
The wall wart adapter is a 42V 1.5A rated switching converter, listed at 84W max from AC (though output is max 63W). The wall wart does the necessary CC/CV current limiting, with a ~44. | The wall wart adapter is a 42V 1.5A rated switching converter, listed at 84W max from AC (though output is max 63W). The wall wart does the necessary CC/CV current limiting, with a ~44.15V open circuit voltage output when no battery is connected. Output is switched to the battery though a "GS3MR HCH" diode, switched by a AP9575GH-HF P-channel MOSFET (60V 15A 90mΩ @12A). | ||
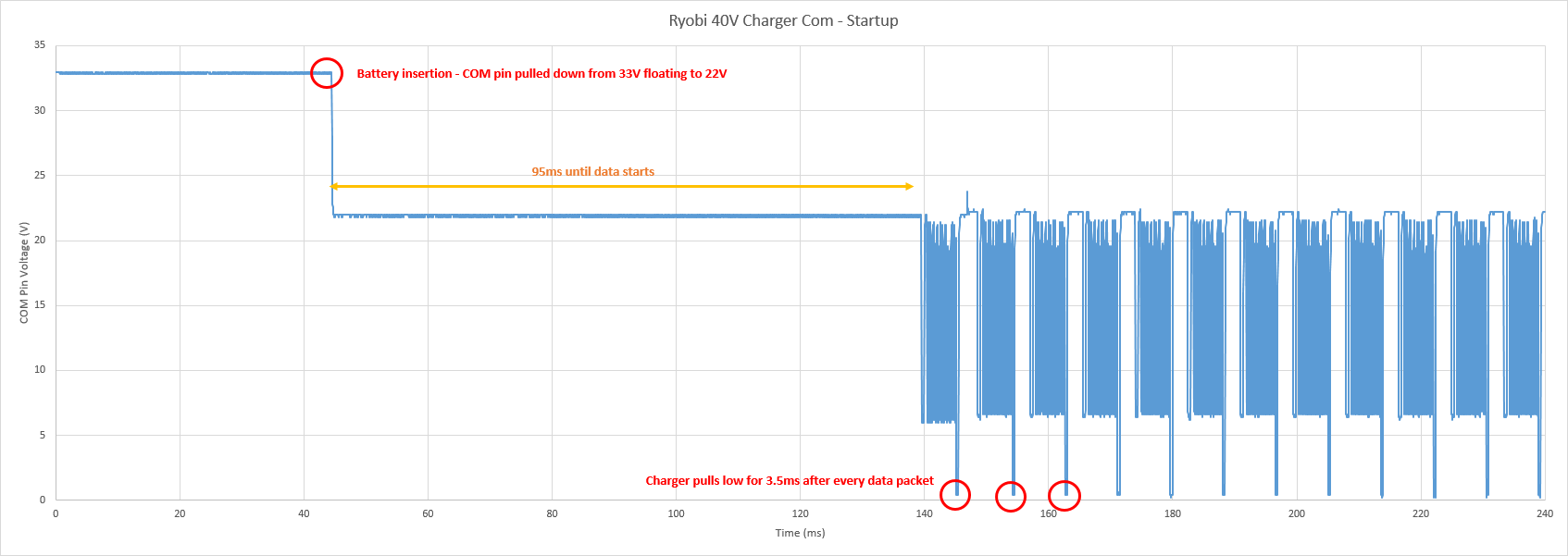
Charging Sequence: | Charging Sequence: | ||
[[File:Ryobi_40VChg_Sequence_Main. | [[File:Ryobi_40VChg_Sequence_Main.png|thumb|center|400px|Battery insertion to charging start sequence.]] | ||
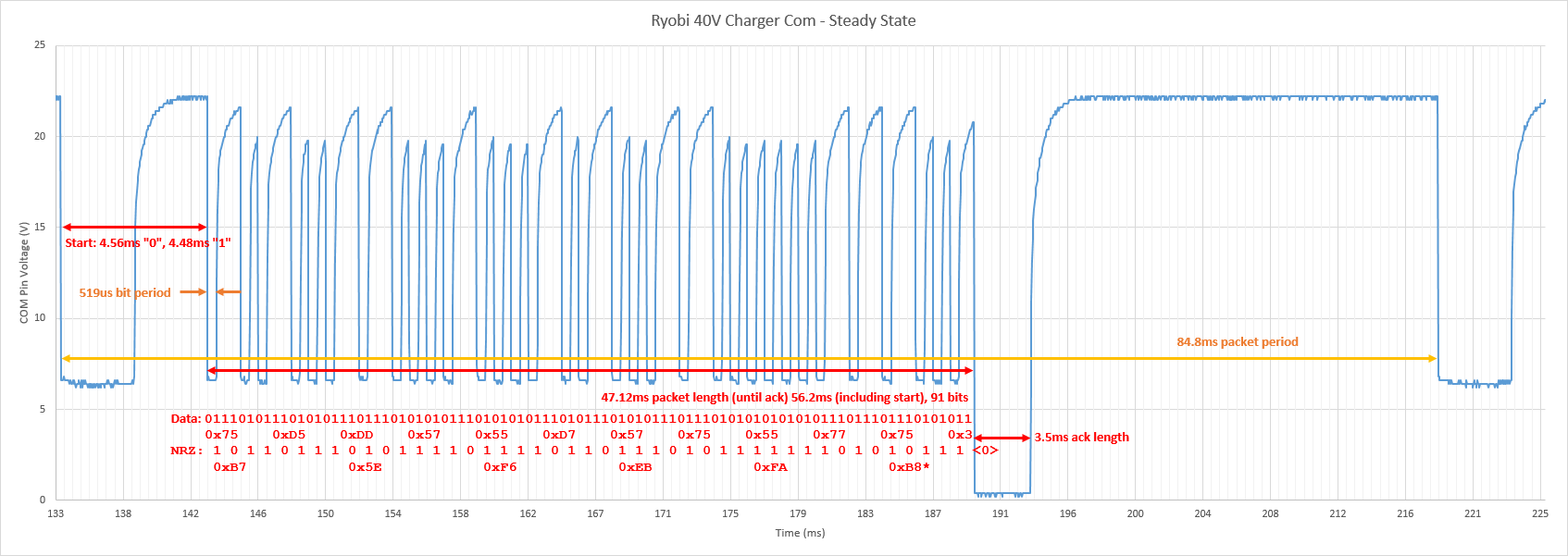
Data detail: | Data detail: | ||
[[File:Ryobi_40VChg_Packet. | [[File:Ryobi_40VChg_Packet.png|thumb|center|400px|Data packet detail.]] | ||
The charger includes a 5V 1.5A buck based on a MP2487 (4.5-55V in, 220mOhm PFET, 1.5A max). The sticker claims 5V 2.1A output. | |||
There is also a resistor bank of 10 ohms effective (5p 130 ohms SMD series 5p 130 ohms SMD, in parallel with 5p 62 ohms 3-5W through hole), which is switched on to the pack to test IR, through a SW088R06VT N-channel MOSFET (60V 40A 9.2mΩ @20A). | |||
The charger is controlled by an NXP LPC824M201JHI33E 32-bit 30 MHz Cortex M0 MCU. | |||
Latest revision as of 21:57, 13 August 2019
This is a basic analysis of how a Ryobi 40V smart charger (model number OP403) communicates with the battery's BMS to enable the charging FET.
Electronics
Pictures of the charger PCB are below:
The wall wart adapter is a 42V 1.5A rated switching converter, listed at 84W max from AC (though output is max 63W). The wall wart does the necessary CC/CV current limiting, with a ~44.15V open circuit voltage output when no battery is connected. Output is switched to the battery though a "GS3MR HCH" diode, switched by a AP9575GH-HF P-channel MOSFET (60V 15A 90mΩ @12A).
Charging Sequence:
Data detail:
The charger includes a 5V 1.5A buck based on a MP2487 (4.5-55V in, 220mOhm PFET, 1.5A max). The sticker claims 5V 2.1A output.
There is also a resistor bank of 10 ohms effective (5p 130 ohms SMD series 5p 130 ohms SMD, in parallel with 5p 62 ohms 3-5W through hole), which is switched on to the pack to test IR, through a SW088R06VT N-channel MOSFET (60V 40A 9.2mΩ @20A).
The charger is controlled by an NXP LPC824M201JHI33E 32-bit 30 MHz Cortex M0 MCU.