Ryobi40V: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "This is a basic analysis of how a Ryobi 40V smart charger (model number OP403) communicates with the battery's BMS to enable the charging FET. ==Electronics== Pictures of the...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
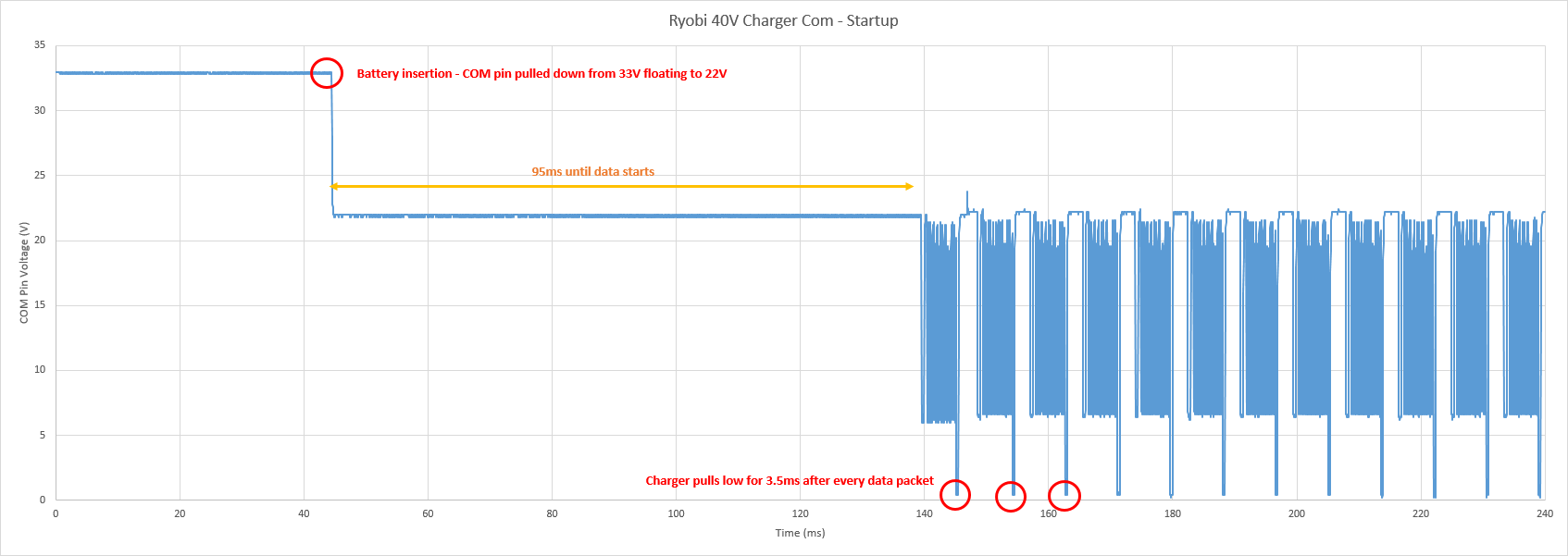
Charging Sequence: | Charging Sequence: | ||
[[File:Ryobi_40VChg_Sequence_Main. | [[File:Ryobi_40VChg_Sequence_Main.png|thumb|center|400px|Battery insertion to charging start sequence.]] | ||
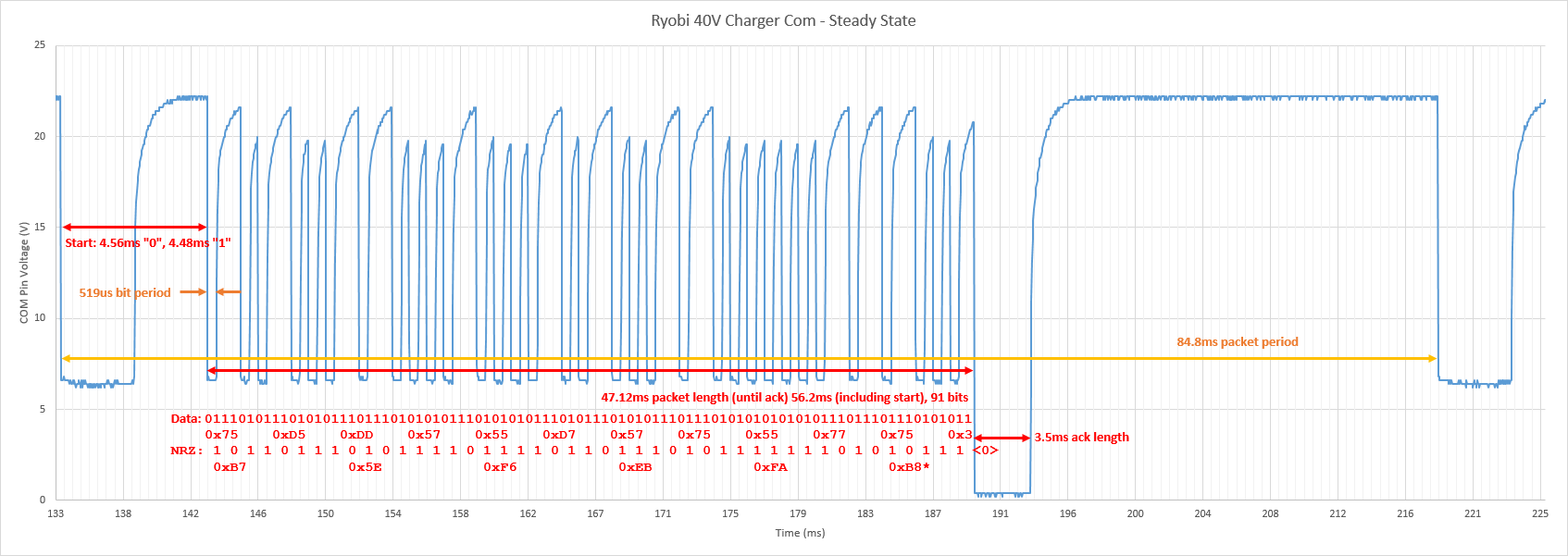
Data detail: | Data detail: | ||
[[File:Ryobi_40VChg_Packet. | [[File:Ryobi_40VChg_Packet.png|thumb|center|400px|Data packet detail.]] | ||
The charger includes a 5V 1.5A buck based on a MP2487 (4.5-55V in, 220mOhm PFET, 1.5A max). The sticker claims 5V 2.1A output. | |||
Revision as of 00:19, 13 August 2019
This is a basic analysis of how a Ryobi 40V smart charger (model number OP403) communicates with the battery's BMS to enable the charging FET.
Electronics
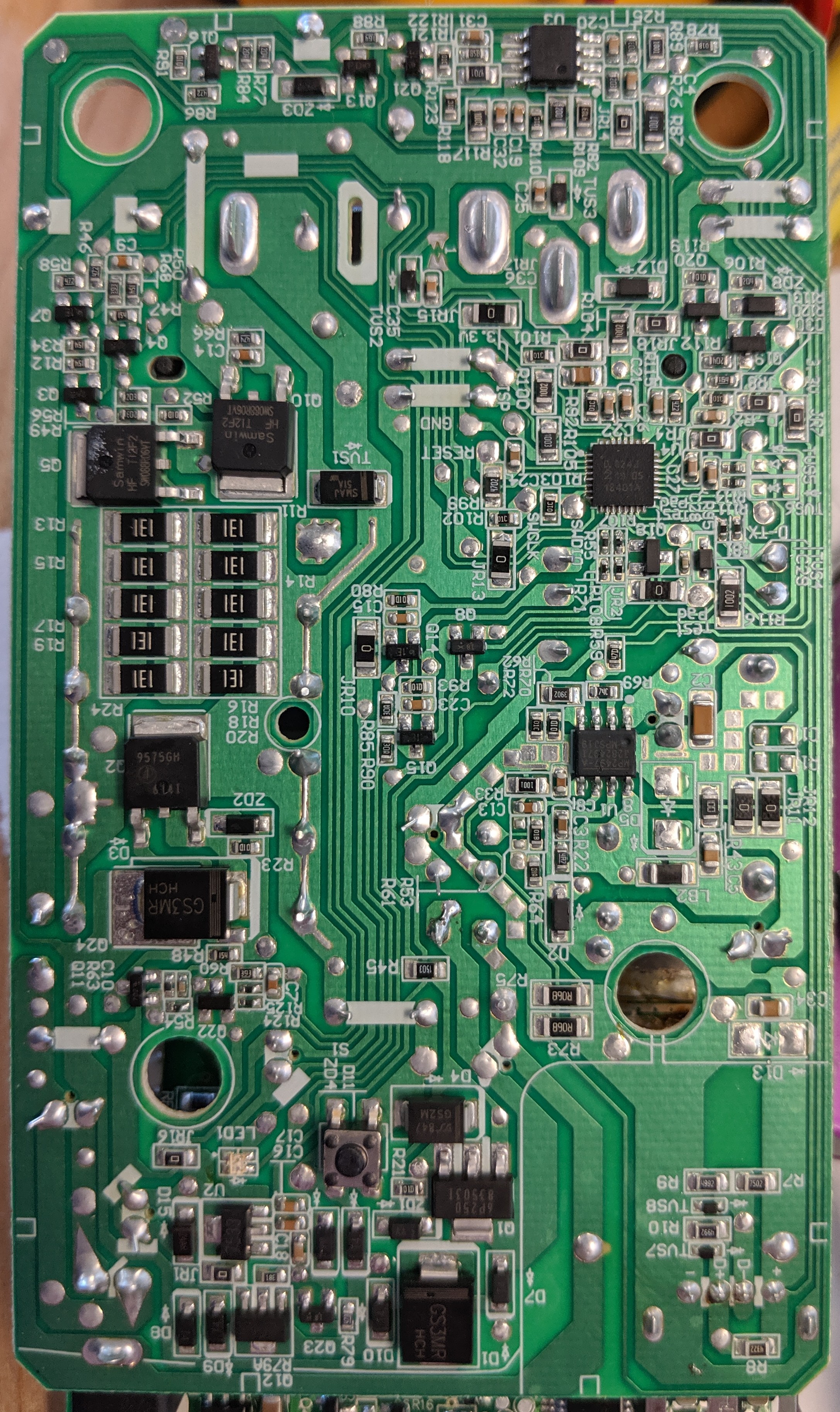
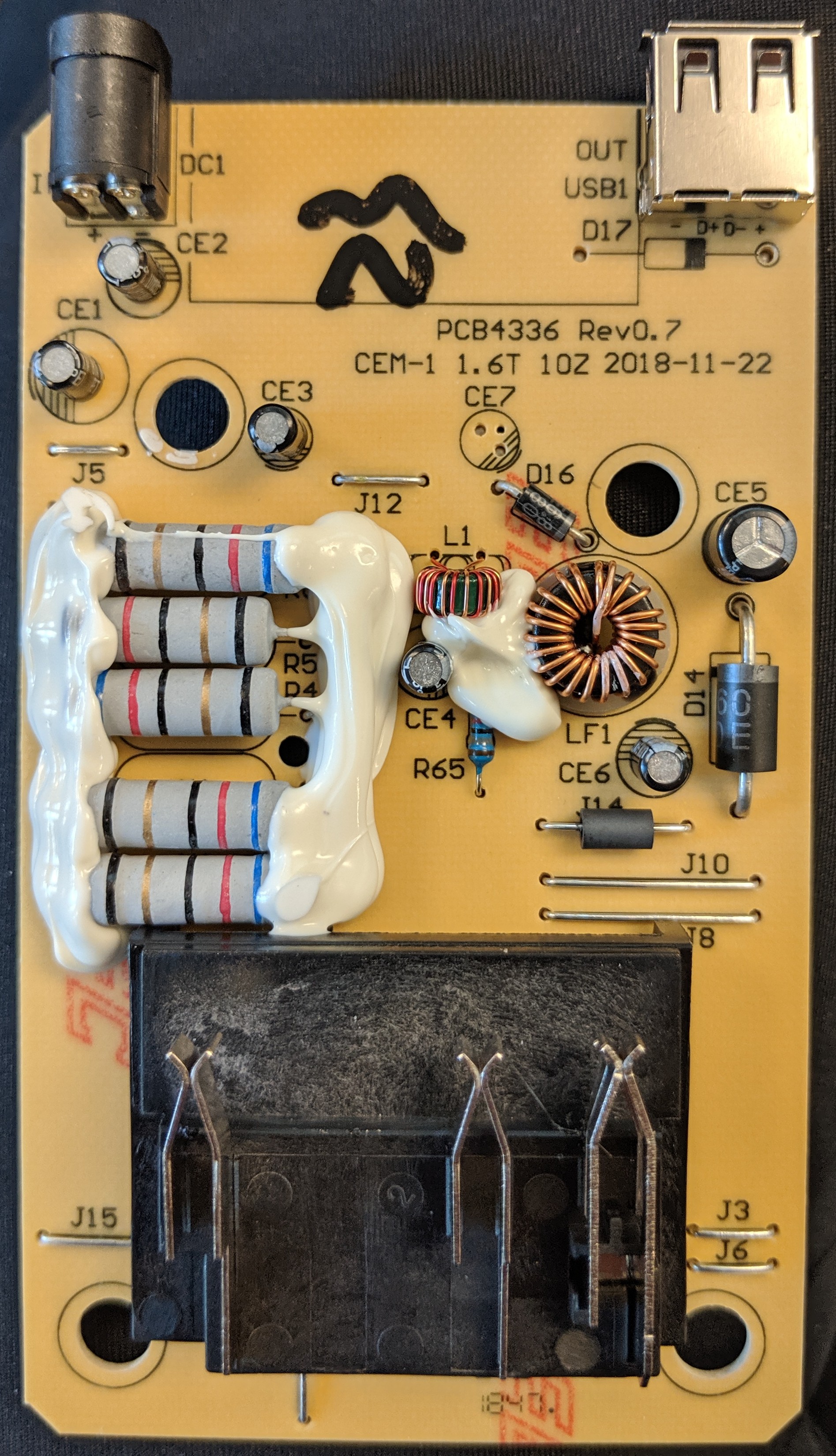
Pictures of the charger PCB are below:
The wall wart adapter is a 42V 1.5A rated switching converter, listed at 84W max from AC (though output is max 63W). The wall wart does the necessary CC/CV current limiting, with a ~44.2V open circuit voltage output when no battery is connected. Output is switched to the battery though a MOSFET.
Charging Sequence:
Data detail:
The charger includes a 5V 1.5A buck based on a MP2487 (4.5-55V in, 220mOhm PFET, 1.5A max). The sticker claims 5V 2.1A output.